How to test your Rest/Graphql/Soap API or view others APIs without the terminal?

Photo by Daria Volkova on Unsplash
Say, you have made a REST API and want to test it? There is a terminal cli called curl but it can become a pain to learn all those commands. So, what can you use?
What is Postman?
Postman is a collaborative API-development tool to streamline collaboration so you can make better APIs-faster.
What can you fo with Postman?
- You can send REST, GRAPHQL, SOAP, requests directly from Postman
- You can add automated testing for your app with CI/CD pipelines to ensure that changes to your code does not break API in production
- Gives you API-first development freedom
- Generate documentations for your API
- Collaborate with others
Download Postman
Visit this link, postman.com/downloads to download the Postman GUI.
How to use Postman to make requests to an endpoint?
For testing purposes we'll be using JSONPlaceholder which gives you a free api for testing your frontend code or prototyping
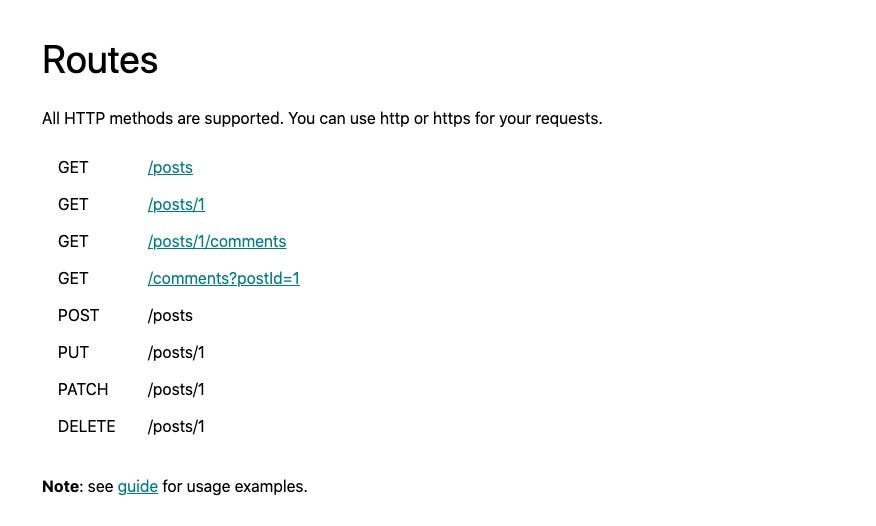 This is what the JSONPlaceholder website tells us. So let's get to it!!
This is what the JSONPlaceholder website tells us. So let's get to it!!
Making a GET Request
Let's try out the very first api as listed in the website. JSONPlaceholder gives a lot more data like Users, posts, albums, photos, etc but we'll be using the posts api

So according to the website, we need to make a request to jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts to list all the posts
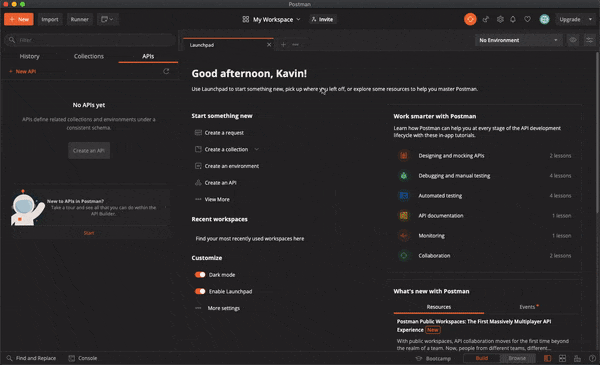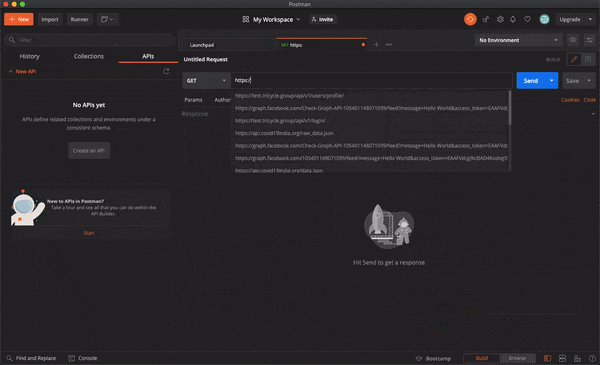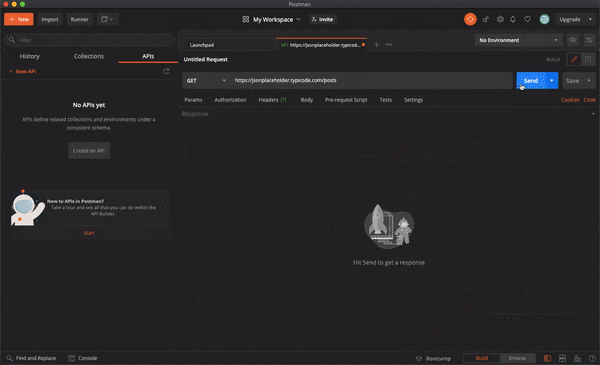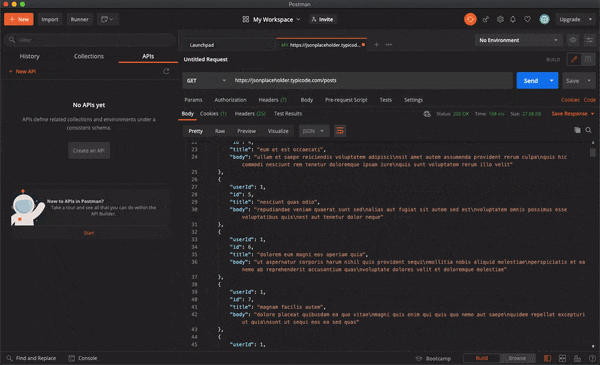
Making a GET Request is quiet easy but making a POST Request gets a little tricky even though the Postman UI is very simple and is very self-explanatory
Making a POST Request
As given in the JSONPlaceholder website, the url remains the same, but we send a post request. So in the dropdown, select POST
In a POST request, we usually send what is called a payload or a request body. The way we send that in Postman is like this, go to the Body tab and click on raw. In the dropdown which just came, select, JSON, and paste this
{
"title": "foo",
"body": "bar",
"userId": 1
}
and you should get a response like this
{
"title": "foo",
"body": "bar",
"userId": 1,
"id": 101
}
So, that is how you send a POST request.
Other request types like DELETE, PUT, etc are quite similar to these two, so you would now be able to make requests with Postman. But in real life applications, the API's might be protected by Authentication. So, it's sometimes sent in the header(Click on the Headers tab and add the header as given in the api) or sent in cookies. For the latter, Fortunately for us, Postman manages it by itself, so you don't need to do anything
I would suggest that you go through the interface of Postman, and try to experiment with the different options given. 👍
